What is a Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine?
Industry News-In the intricate world of metal casting, the creation of a hollow or complex metal component begins not with the metal itself, but with a precisely formed core. These cores, typically made of sand bonded with resin, define the internal passages of a cast part, such as the coolant jackets in an engine block or the intricate cavities inside a pump housing. The machine responsible for mass-producing these essential sand forms with high precision and efficiency is the core shooter. Among the various designs, the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine represents a specific and highly effective configuration for a wide range of core-making applications. Understanding its principle, advantages, and typical applications is key to appreciating its role in modern foundries.
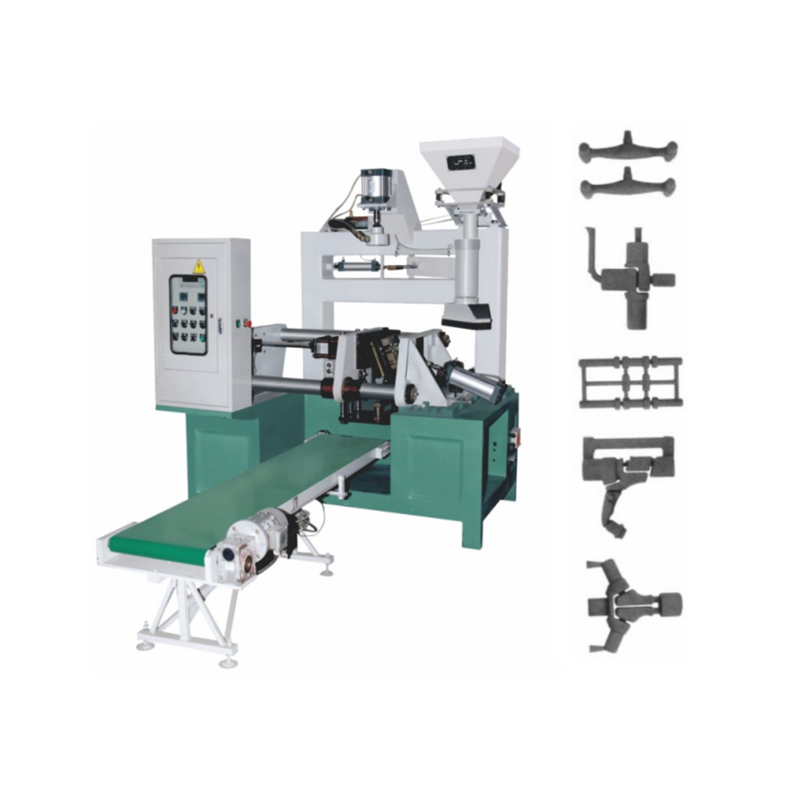

Fundamental Operating Principle and Design
The term "vertical parting" directly describes the machine's core mechanical action. Unlike horizontal machines where the two halves of the mold (the core box) separate sideways, this machine's design is defined by a vertical separation.
-
- Vertical Parting Action: The core box, which is the negative impression of the desired core, is mounted onto two parallel plates. One plate is fixed, while the other is movable. The machine's mechanism drives the movable plate in a vertical plane, opening and closing the core box like a book standing on its spine. This vertical movement is a defining characteristic of the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine.
- The Shooting Process: In the closed position, the sand-resin mixture is propelled—or "shot"—at high pressure from a shooting head into the cavity of the core box. The pressure ensures the sand is densely and uniformly packed into every detail of the core box. The design of the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine often allows for gravity to assist in the filling process, contributing to consistent core density.
- Curing and Ejection: After shooting, the core box, with the packed sand inside, is often moved to a curing station where the resin binder is activated, typically by heat (from gas catalysts or electric heaters), solidifying the core. Once cured, the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine opens vertically, and ejection pins gently push the finished core out, ready for the casting process.
This vertical approach to parting and core formation offers several distinct benefits that make it a preferred choice for many production scenarios.
Key Advantages and Operational Benefits
The specific architecture of a vertical parting machine translates into tangible benefits for foundry operations, impacting everything from floor space to core quality.
-
- Optimized Floor Space and Gravity Assistance: The vertical footprint of the machine is generally more compact than that of a horizontal machine with a similar capacity. This efficient use of floor space is a significant advantage in crowded production environments. Furthermore, the vertical orientation allows gravity to work in harmony with the shooting process, helping to minimize air pockets and ensuring a more consistent fill, especially for simpler core geometries.
- Simplified Automation and Handling: The vertical parting action lends itself well to automated material handling systems. Robots can easily access the parting line to place inserts or extract finished cores from the open mold. The clear, upright access simplifies the integration of the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine into a fully automated core-making cell, streamlining the workflow from core production to the assembly of the final mold.
- Reduced Sand Spillage and Efficiency: The design can contribute to a cleaner working environment. The vertical shooting and parting action can be engineered to minimize sand spillage during the box closing and opening cycles. When combined with its potential for high cycling speeds, the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine becomes a reliable source of high-volume core production with excellent efficiency and minimal waste.
Common Applications and Production Scenarios
The versatility of the vertical parting design makes it suitable for a broad spectrum of casting applications, though it excels in particular areas.
-
- High-Volume Production of Small to Medium Cores: This machine type is exceptionally well-suited for foundries that need to produce large quantities of small to medium-sized cores. Examples include cores for automotive components like brake calipers, engine brackets, and valve bodies. The speed and reliability of a Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine make it an economic backbone for such high-demand production lines.
- Cores with Simple to Moderate Complexity: While capable of producing complex cores, the vertical design is often the machine of choice for cores that do not require an excessive number of complex, horizontally-acting slides and pullbacks. Its strength lies in the efficient and rapid production of cores where the primary movement is a straightforward vertical open-and-close.
- Compatibility with Various Binder Systems: The fundamental shooting and parting process of the vertical machine is adaptable. It can be effectively used with different sand binder systems, including the widely adopted cold-box process (where a gas is passed through the sand to cure it) and shell core processes. This flexibility allows foundries to utilize the Vertical Parting Core Shooting Machine across different production requirements without changing the core molding technology.
 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Deutsch
Deutsch