The Development of Gravity Casting Machine
Industry News-A gravity casting machine operates on a relatively straightforward principle: molten metal is poured into a mold under the force of gravity. Unlike high-pressure systems, this approach allows for a more controlled and less turbulent filling process. This method is particularly well-suited for non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper alloys, and certain magnesium-based materials.
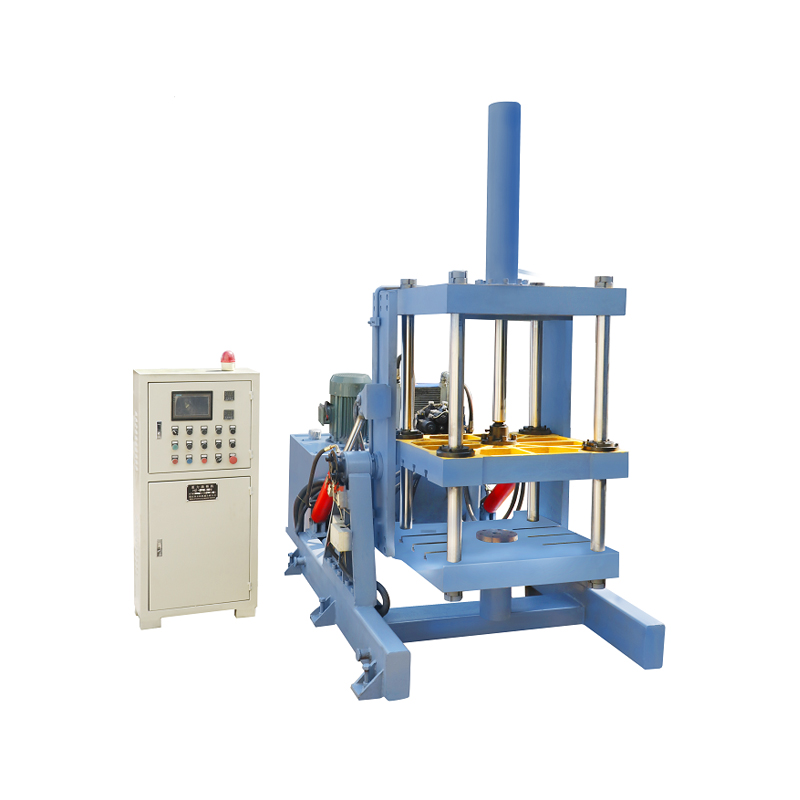

Early versions of the gravity casting machine were manually operated and heavily dependent on the operator’s skill. The casting quality varied significantly, as minor differences in pouring speed, mold temperature, and handling technique had a noticeable impact on the final product. Over time, however, the need for improved consistency and increased volume production led to mechanized systems with enhanced control features.
Modern gravity casting machines have evolved into semi-automatic or fully automatic systems. These machines are equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs), temperature regulation units, and automated pouring arms. Such additions ensure uniform mold filling and reduce human error. From the manufacturer’s standpoint, these advancements have resulted in higher repeatability and improved overall efficiency.
One of the reasons manufacturers continue to invest in the gravity casting machine is its suitability for creating complex geometries with minimal defects. The low-turbulence filling process reduces porosity and improves the mechanical properties of the finished casting. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and general engineering frequently specify parts made with this method because of the consistent structure and dimensional stability it offers.
Another key development in the gravity casting machine has been the integration of real-time monitoring systems. Sensors now track key process variables such as metal temperature, mold temperature, and pouring duration. These parameters are logged and analyzed to ensure that each cycle maintains consistent quality. If deviations are detected, corrective actions can be initiated automatically. This level of process transparency is critical for manufacturers focused on meeting strict quality control requirements.
In addition to hardware improvements, mold technology has also advanced alongside the gravity casting machine. Permanent metal molds, often made from cast iron or steel, have replaced many traditional sand molds. These permanent molds can be reused hundreds or even thousands of times, making them more suitable for medium to large-scale production. The compatibility between modern mold materials and casting machines has enhanced part accuracy and surface finish.
Energy efficiency has become another point of focus in the development of the gravity casting machine. With rising energy costs and increased attention to environmental sustainability, many manufacturers are turning to machines designed with optimized thermal systems. These systems minimize energy loss during the melting and pouring phases, helping to reduce operational expenses without compromising output quality.
Safety is also a major consideration in current designs of the gravity casting machine. Modern equipment often includes protective barriers, emergency stop systems, and heat-resistant coatings to ensure operator safety. Proper ventilation and fume extraction are integrated into machine design, especially in enclosed foundry environments.
Maintenance and serviceability are further areas where progress has been made. The gravity casting machine is now designed with modular components that allow for quicker part replacement and easier diagnostics. This is beneficial for manufacturers aiming to reduce downtime and improve machine availability.
Looking ahead, the gravity casting machine is likely to continue evolving, particularly in the areas of automation and digital connectivity. Integration with factory management systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and data-driven process optimization are areas already seeing research and application. As smart manufacturing becomes more mainstream, the gravity casting machine will play a key role in bridging traditional foundry processes with modern industrial technologies.
 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Deutsch
Deutsch