Coated Sand Casting Molds: Types, Uses, and Practices
Industry News-Coated sand casting molds are essential tools in the metal casting process, where molten metal is poured into molds to create components with precise shapes. This casting technique utilizes a combination of sand and a coating material, typically a ceramic or a type of binder, to form a mold that can withstand high temperatures and ensure quality results.
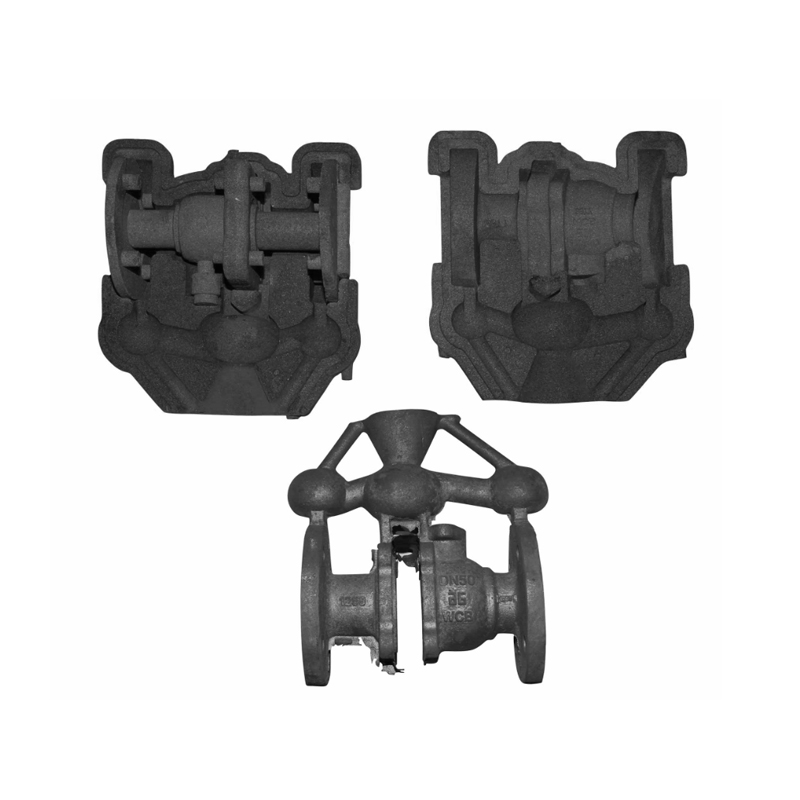

What Are the Common Types of Coated Sand Casting Molds?
Coated sand molds are made by coating the surface of a sand mold with a ceramic or other heat-resistant material. These molds are designed to handle high-temperature metals and produce high-precision parts. Here are the common types:
Shell Molds:
These molds are created by first coating a sand mold with a fine layer of ceramic or silica. The coating is then hardened and the mold is heated to create a shell. This shell helps to improve the precision and surface finish of the cast part.
Green Sand Molds:
These molds are made by mixing sand with a binder (typically clay) and water, forming a mold that is then coated with a heat-resistant material. This is a traditional method used for casting metals with relatively lower melting points.
Dry Sand Molds:
These molds are made by drying the sand after it is coated with a heat-resistant material. Dry sand molds provide a stronger and more durable mold, which is ideal for metals with high melting points, such as steel or iron.
Lost Foam Molds:
In this technique, a foam pattern is coated with a fine sand mixture and then covered with a heat-resistant coating. The foam evaporates when molten metal is poured in, leaving behind a precise casting.
Coated Sand Casting Mold is Commonly Used in…
Coated sand casting molds have wide-ranging applications across various industries. Their ability to create high-precision parts makes them suitable for casting metals used in machinery, automotive, aerospace, and artistic applications. The following are typical uses for coated sand molds:
1. Aerospace Components:
Complex Geometries: The aerospace industry often requires parts with intricate shapes that cannot easily be produced by other casting methods. Coated sand casting molds allow for the creation of complex, lightweight, and high-strength components, such as turbine blades and structural elements of aircraft.
2. Automotive Industry:
Engine Parts and Components: Coated sand casting molds are commonly used in the production of automotive engine parts, including cylinder heads, intake manifolds, and pistons. The precision and strength provided by coated molds ensure that these parts meet the high-performance standards required by the automotive industry.
3. Industrial Equipment:
Heavy Machinery Parts: The ability to cast large, durable components with high resistance to wear makes coated sand casting molds ideal for manufacturing parts for heavy machinery, such as gears, crankshafts, and housings.
4. Artistic and Decorative Items:
Sculpture and Castings: Coated sand casting molds are also used in the art world, where artists cast sculptures and decorative items. The fine detail and surface finish achievable with these molds make them a popular choice for artists seeking to reproduce intricate designs.
5. Medical Devices:
Precision Casting for Medical Equipment: Medical device manufacturers use coated sand molds to produce highly accurate components, such as implants and surgical instruments, where precision and strength are crucial.
Notes on Using Coated Sand Casting Molds
Using coated sand casting molds requires attention to detail and careful consideration of the materials, processes, and safety precautions. Here are some important notes for successful mold usage:
- Material Selection:
Choose the right sand and binder material for the specific type of metal being cast. For example, silica sand is ideal for casting ferrous metals, while zircon sand is used for non-ferrous metals.
Ensure that the coating material is compatible with the casting metal’s temperature to avoid mold damage or contamination.
- Mold Preparation:
Properly prepare the sand mold before coating. Ensure that the mold is free from moisture and impurities, as these can negatively impact the quality of the cast.
Apply the coating evenly and allow sufficient time for drying and hardening. Incomplete curing can result in poor mold strength or dimensional inaccuracies.
- Temperature Control:
Monitor the mold’s temperature during the casting process. Coated sand molds are designed to withstand high temperatures, but excessive heat can cause deformation. Proper temperature control will ensure that the mold retains its shape and that the cast part is formed accurately.
- Ventilation and Airflow:
Ensure proper venting in the mold to allow gases to escape during the pouring of molten metal. Poor ventilation can lead to air pockets, gas porosity, or even cracks in the final casting.
- Post-Casting Cleaning:
After the casting process, clean the mold carefully to remove any remaining sand and coating material. This will help maintain mold quality for future use and ensure smooth surface finishes on the final product.
- Safety Measures:
Always wear appropriate protective gear when handling hot molds and molten metal. Safety goggles, heat-resistant gloves, and protective clothing are essential to avoid burns and other injuries.
Work in a well-ventilated area, especially when working with coatings that may release fumes or when handling metals with high melting points.
 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Deutsch
Deutsch