What Is Coated Sand Casting Mold and How Does It Work?
Industry News-What Is Coated Sand Casting Mold and How Does It Work?
Coated sand casting mold refers to a sand mold that has been coated with a refractory or binding layer. This coating can be applied to the sand mold surface using a variety of materials such as sodium silicate, resin, or ceramic coatings. The primary purpose of coating is to improve the mold's surface quality and thermal resistance.
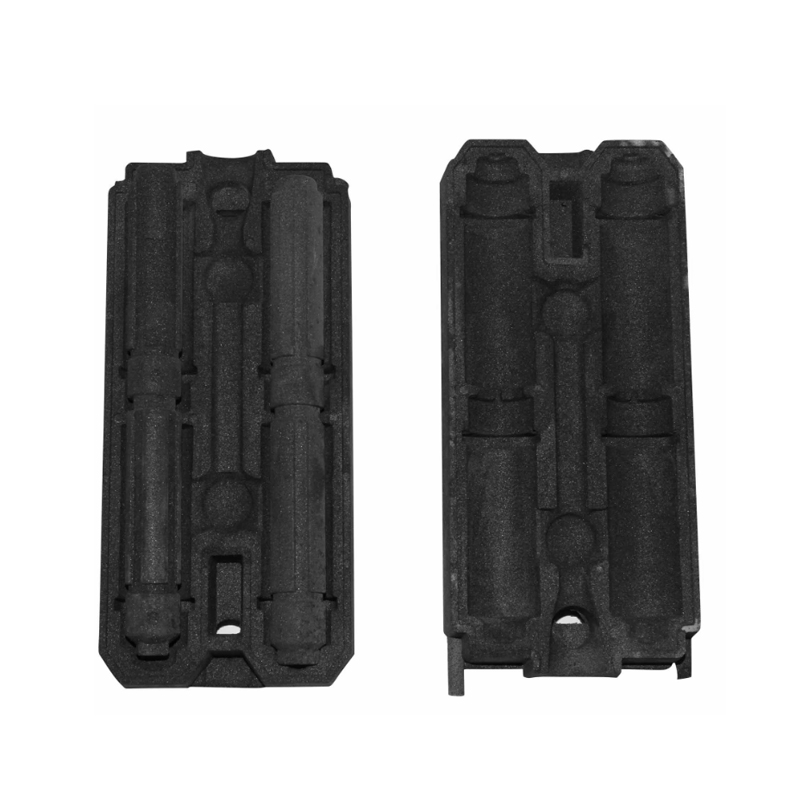

The working process typically includes:
Mold Preparation: The sand mold is formed using a pattern, and the mold cavity is shaped according to the casting design.
Coating Application: A thin layer of coating material is applied to the mold cavity surface. The coating can be sprayed, brushed, or applied using automated equipment.
Drying and Curing: The coated mold is dried or cured to form a stable surface layer.
Pouring Molten Metal: Molten metal is poured into the mold cavity. The coating helps prevent sand erosion and reduces gas defects.
Cooling and Solidification: The casting cools and solidifies inside the coated mold.
Shakeout and Cleaning: The casting is removed, and the coating and sand residues are cleaned off.
What Are the Key Benefits of Coated Sand Molds?
Improved Surface Finish: Coated sand molds produce smoother surfaces on cast parts, reducing the need for extensive machining.
Reduced Sand Defects: The coating layer helps prevent sand erosion and minimizes sand inclusion defects in the casting.
Better Dimensional Accuracy: Coatings help maintain cavity shape during pouring and solidification, improving dimensional stability.
Enhanced Thermal Resistance: Refractory coatings provide better heat resistance, supporting consistent solidification and reducing thermal cracking.
Lower Gas Porosity: Certain coatings help reduce gas generation from sand, improving casting quality.
Improved Mold Strength: Coated layers increase mold strength and resistance to mechanical damage during handling and pouring.
Cost Efficiency: Improved surface quality and reduced defects can lower downstream processing costs and improve yield.
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Coating?
Coating materials for sand molds vary based on casting requirements and the type of sand mold. Common coating materials include:
Sodium Silicate-Based Coatings: Used for improved surface finish and reduced permeability. They are suitable for many general casting applications.
Resin-Based Coatings: Provide strong adhesion and better thermal stability. Commonly used in higher-temperature casting processes.
Ceramic Coatings: Offer superior heat resistance and are used for high-temperature alloys and complex castings.
Zircon and Alumina Additives: These materials are often mixed into coatings to improve refractoriness and prevent metal penetration.
Water-Based or Solvent-Based Coatings: Depending on environmental and production considerations, foundries may choose water-based coatings for lower emissions or solvent-based coatings for faster drying.
What Are the Common Challenges and How Are They Addressed?
Common challenges in coated sand casting molds include coating defects, uneven coating thickness, and thermal cracking. These issues can be addressed by:
Controlling Coating Thickness: Use consistent spraying or brushing methods and automated equipment to ensure uniform coating.
Optimizing Drying and Curing: Ensure proper drying time and temperature to avoid cracking or delamination of the coating.
Improving Sand Quality: Use clean sand with controlled moisture content to reduce defects and improve coating adhesion.
Monitoring Mold Temperature: Maintain stable mold temperature to reduce thermal shock and cracking during pouring.
Regular Quality Inspection: Inspect coated molds for surface defects before pouring and adjust coating parameters as needed.
 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Deutsch
Deutsch