What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of The Shell Core Machine?
Industry News-What are the operational advantages of the shell core machine?
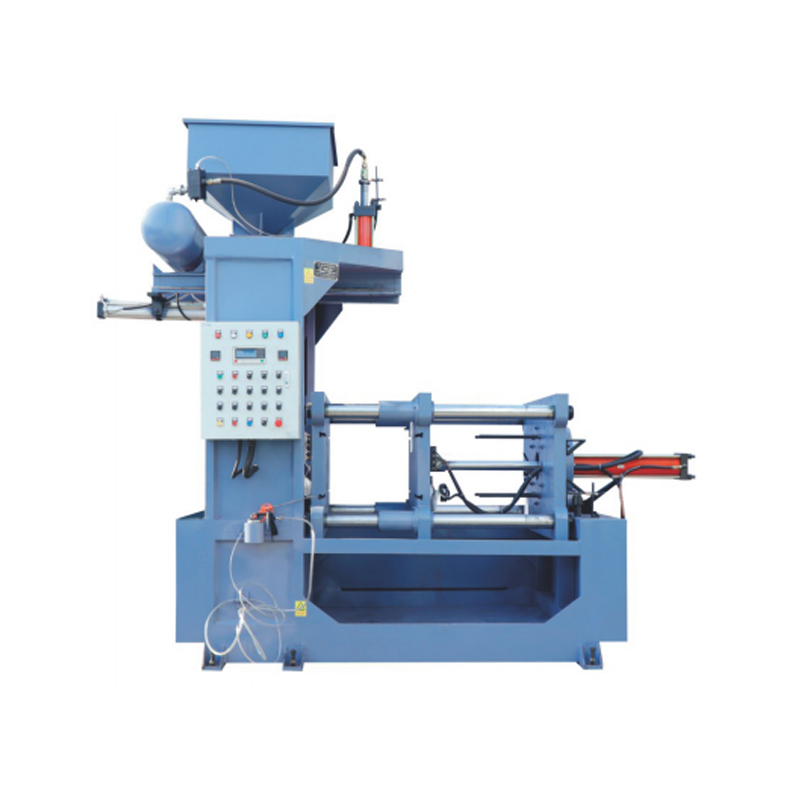

The shell core machine offers several operational advantages that enhance efficiency in foundry production. These benefits relate to speed, consistency, and labor reduction:
- Consistent Core Production: The machine produces uniform sand cores with accurate dimensions, reducing errors that could occur with manual core making. Consistency is crucial for maintaining quality in casting operations.
- Reduced Labor Intensity: Automation minimizes the need for extensive manual handling. Operators are primarily responsible for setup and monitoring, while the machine performs repetitive coating and baking cycles.
- Faster Production Cycle: Compared to traditional hand-core production, shell core machines accelerate the creation of complex cores. The controlled heating and coating process ensures quicker curing times.
- Precision in Complex Shapes: The machine can handle cores with intricate internal structures, which might be difficult to produce manually. This allows foundries to produce components with more detailed and consistent internal geometries.
These operational advantages contribute to improved workflow efficiency and reliability in casting production, particularly when producing high volumes of cores.
What are the quality-related benefits of using a shell core machine?
Beyond efficiency, the shell core machine offers quality advantages that impact casting outcomes:
- Smooth Surface Finish: The controlled application of sand and resin ensures a smooth core surface, reducing the need for post-casting finishing work.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Automated coating and heating allow for precise control of core thickness, which helps maintain dimensional accuracy in the final castings.
- Reduced Core Breakage: Uniform strength throughout the core decreases the likelihood of breakage during handling or casting, waste and improving yield.
- Enhanced Reproducibility: The machine enables consistent reproduction of identical cores across batches, supporting reliable mass production.
- These quality-related benefits make the shell core machine suitable for applications where precision and reproducibility are critical.
What are the operational disadvantages of the shell core machine?
Despite its advantages, the shell core machine has limitations that should be considered when planning foundry operations:
High Initial Cost: The purchase and installation of a shell core machine involve significant capital investment, which may be prohibitive for small-scale foundries.
Energy Consumption: The machine requires continuous power to heat patterns and cure cores, contributing to higher energy costs compared to manual core making.
Maintenance Requirements: The mechanical and heating components require regular maintenance to ensure consistent performance, adding to operational overhead.
Limited Flexibility for Small Batches: While efficient for mass production, the machine may be less economical for small or custom batches due to setup and heating time.
These operational disadvantages highlight the importance of evaluating production volume and cost before investing in the equipment.
What are the technical or material-related limitations?
The shell core machine also presents technical considerations related to material properties and operational constraints:
- Resin Dependency: The machine relies on resin-coated sand, which may limit the choice of sand types and add material costs.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Variations in heating can affect shell strength and core integrity, requiring careful monitoring.
- Complexity in Adjustments: Adjusting the machine for cores of different sizes or shapes may require recalibration, which can slow production for varied orders.
- Understanding these technical limitations is necessary for proper planning and for ensuring the quality of the final castings.
 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Deutsch
Deutsch